In the last post we cast an appraising eye over the graphs we made using NodeXL Basic (a product of the ‘Social Media Research Foundation’). In this post, you’ll see some of the features of that may help calm a busy graph. Pick and choose from them as appropriate to you tree, research aims and aesthetic preferences.
If you haven’t made a graph yet, see the index to this series for earlier posts.
Display settings
Take it one group at a time
Once you’ve made groups, you can move to the Groups worksheet and enter ‘skip’ in the Visibility column for each group except the one(s) that you’re interested in. Click Refresh, and only the unskipped groups will be shown. You can also view a few groups at a time as I did in the previous post.
Reduce edge opacity
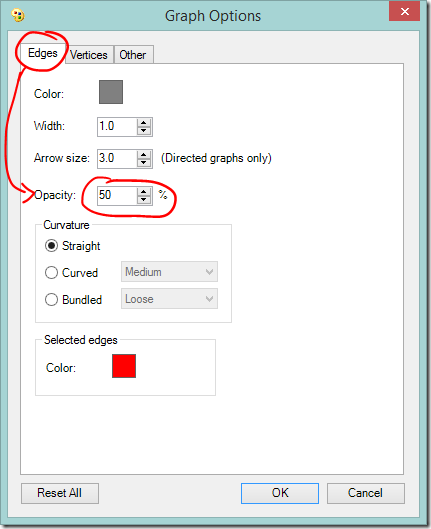
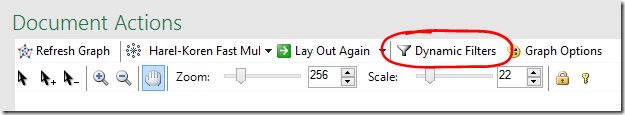
If there are a lot of crossing lines it might be easier to work with the graph if you reduce the line opacity. You can change the defaults used for the graph, including the edge opacity via the Graph Options button.
- Click the Graph Options button
- Lower the default Edges Opacity – the lower the opacity, the more transparent the line.
This may not remove as much visual clutter as you want, but if the dots appear to be sitting on a blanket of grey it may help you see some structure.
Swap labels for tooltips
In Part 3 we used the Autofill columns button on the NodeXL ribbon to add labels to the graph. For a busy graph you may prefer to use same button to clear the labels column and set the tooltip to ‘name’. That way you’ll see the match’s name by hovering over their dot.
Grouping
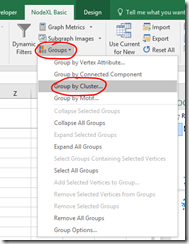
If your groups don’t break up nicely, try a different clustering algorithm.
- On the NodeXL Ribbon select Groups, Group by Cluster…
- Select an option from those presented and click OK. The calculations may take some time for a complex graph.
- Refresh Graph to apply the new groupings.
Clauset-Newman-Moore clustering algorithm
Same graph with Wakita-Tsurumi clustering algorithm
Remember that these algorithms were not created with your DNA results in mind! Hopefully one of them will work well with your data – but don’t assume that because it sounds scientific it must be right.
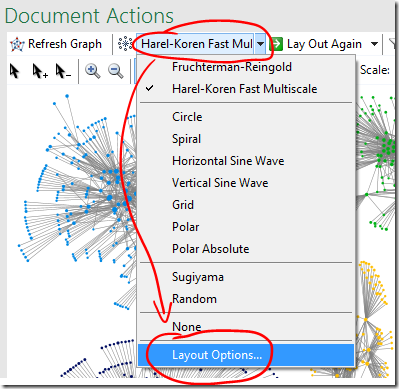
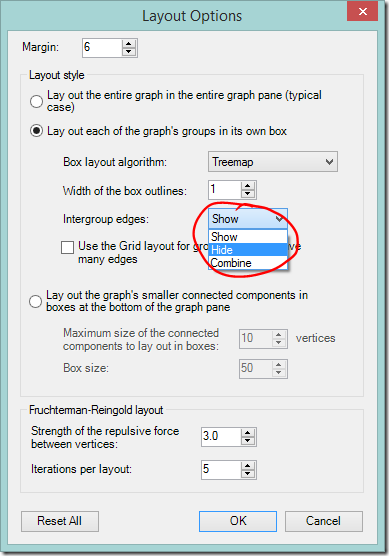
Try a different group box layout – or none at all
- Different group box layout options are available under ‘Layout Options’ on the graph area or main NodeXL ribbon, bottom item Layout Options…
‘Force-directed’ box layout algorithm used, box edge width 0 (I.e. no line)
Hide intergroup connections
It’s possible to hide all the the lines that run between different groups. This instantly cleans up a graph and makes connections within a group easier to see, but does so at the expense of between-group information.
- Click the Layout options dropdown on the NodeXL Ribbon or the graph area toolbar.
- Change Intergroup edges to ‘Hide’.
Intragroup edges hidden
The graph with between group edges hidden is clean and pretty. It’s easier to see relationships within groups – but relationships between groups are not visible. Again, that reminder that the grouping algorithms were not designed for your DNA data. Those between group connections may be the clue that points you in the right direction.
Alternative: ‘Combine’ is an interesting option to try. It will draw a single, thick line between groups that interlink with each other.
Removing relatives
Skipping close relatives
When we created the Additional Input file we added the word ‘Skip’ to the Visibility column for you and your very close family. The ‘Skip’ direction tells NodeXL not to include that person in the graph, or in the clustering calculations.
It may be helpful to ‘Skip’ some more of your close relatives, especially if PC performance is an issue. Take care though – skipping a relative means the graph loses information.
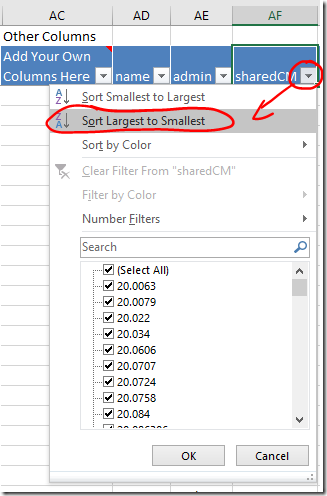
- Your closest relatives are probably at the top of the the Vertices worksheet. If not, sort the sharedCM column from largest to smallest using the dropdown. Your closest relatives will move to the top of the list.
- When you click on the row for a match, the dot that represents that person, and all the lines representing their relationships, will be highlighted in red. This will give you a sense of how widely spread their linkages are, and how much clutter will be cleared (or information lost) by skipping them.
There’s no magic number for the relationship distance or number of links that should be the threshold for skipping people. If I had an aunt and a second cousin who had the same number of links, I might skip the aunt, since theoretically her links are spread over half my tree. I would be much more likely to leave in the second cousin whose matches theoretically sit in a quarter of my tree.
As many readers have realised, you can ‘Skip’ people manually by entering ‘Skip’ in the Visibility column. However, I suggest that you also add the new ‘skip’ line to the Additional Input file as explained in Part 2 (note that the directions on this point have been revised since first posting). If something goes wrong, troubleshooting a large file with complex relationships can be difficult. Keeping the information in a smaller external file makes it easier remember what you’ve done, and allows you to reload or start again if necessary.
Note: After skipping people you might want to rerun your preferred grouping algorithm and refresh the graph.
Skipping children of known matches
It’s not a quick fix, but another category of person that you may want to ‘Skip’ is anyone who is known to be the child of another match. If they are only connected to you on the matching parent’s side you can safely ‘skip’ the child as they, at best, duplicate the parent’s relationship information. Take care that the relationship really is parent-child and not niece or nephew – the information visible to you may look the same in those cases.
Again, I suggest that you at least keep a record of these ‘skips’ outside your main file - the Additional Input file is made for this! If something goes wrong with the graph file, will you really want to track down those relationships again?
Filtering
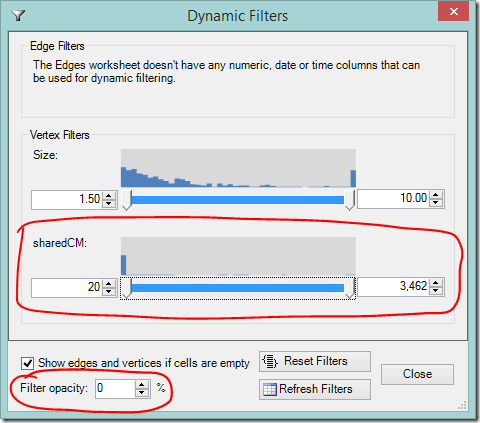
Dynamic Filters allow you to hide your most distant and/or closest relatives.
- Select Dynamic Filters
- Scroll down or expand the window to find the sharedCM slider
- As you adjust the slider’s lower value, your most distant cousins will disappear.
- Adjusting the slider’s upper value will hide your closest cousins (you may need to slide it down a long way).
- If you want to still see the filtered information, but make it less prominent, adjust the filter opacity to your liking.
Wakita-Tsurumi grouping with matches below 15CM filtered out
Excluding matches
If you have a very large number of matches you may decide not to work with distant cousins at all. In this case you could enter ‘Skip’ next to each one, or you could save some time when downloading by using the Filter: 4th Cousin option in the DNAGedcom client.
Deleting smaller matches from the match list, whether before or after importing to NodeXL, won’t help. Matches listed in the in-common-with file will still be included in the graph, you just won’t know who they are!
If you want to go a bit past fourth cousins, but not all the way to those speculative distant matches, filtering or skipping may be a better option than excluding entirely.
Excel tips:
1) If you copy a cell then select multiple cells and paste, the paste value (e.g. ‘Skip’) will be entered into all of the selected cells.
2) Double click on the square at the bottom right corner of a cell to copy it down the page automatically to the next filled box, or the end of the table whichever comes first. It can be a bit fiddly to get the right spot – the curser should change into a black plus sign + without any arrows.
DNAGedcom Note:
There are two versions of the DNAGedcom client being used at present. Version 2 is necessary if you have FTDNA matches, but it doesn’t have the filter option for Ancestry DNA matches (I’m told the option will be reinstated in future). The version linked to in the first post of this series does have the option.
Coming up
In the next post, we’re going to extract more information from the files we already have.




I'm using another approach to busy graph syndrome while I learn the toolset. I have something like 35,000 vertices and 45,000 edge rows. All of the former are my personal DNA matches. The latter are all matches between my matches - I have no edge rows where I map to someone. Since I map literally to everyone, I started out with myself out of the graph (maybe everyone does that). My first instinct was to add 35,000 more edge rows for my own matches, but I decided not to do that and I think it was a good decision so far.
ReplyDeleteI have some specific mysteries I'm trying to resolve with DNA matching. So I start by ensuring each edge row has both the name of the ICW match and the ICW admin. Say I'm studying my known Corey cousins with an eye to finding the parents of our common ancestor John Corey who md Eve Britten. Eve can be excluded from the study because I have known cousin matches with her via her siblings.
I start by filtering on the ICW admin name, removing all choices so there are no edge rows in play. I then select the ICW Admin person who is a known Corey cousin and all her edge rows. I graph and take a look around. That leads me to the next Corey cousin with lots of shared DNA, and I select that person's ICW Admin rows. I repeat this process, regraphing each time, until I either see something new I haven't realized before or the graphs get so cluttered I stop to poke around. I may use scaling or dynamic filters to help with "busy graph" issues. But I don't need to paint the entire set of groups across the 35,000 people in advance and then start removing some. I start small and build up to the point where the people selected are maximally useful. / Tom
Shelley, I want to thank you for the excellent introduction, outline and description of this very powerful tool that you have provided us. I am still feeling my way through graphic analysis but I am starting to get a feel for the process.
ReplyDeleteI too have used a slightly different approach to simplifying a cluttered graph. Following is a description of the successes thus far and the approach I took.
Here is what I have done so far. My second great grandfather on my paternal side has been a roadblock for me. He emigrated from Hesse Germany to the US in 1846, settling in Dayton Ohio where he married another immigrant and lived out his life raising a family of nine children. To this point none of the genealogists in the family have been able to identify the specific location in Germany from whence he came. Unfortunately, most of the kinds of records that might have informed on this point were destroyed in a flood in 1913. Most importantly, those of the church the family attended.
I think that the Nodex graphic analysis that you have so ably provided instructions for, may lead me to an answer. I don’t know whether my approach has been the most efficient path, but I will explain my workflow, in hopes that it will either be useful or will be replaced by a more efficient path.
Starting with 30 groups revealed, I identified the group containing a known second cousin. That group contained 188 vertices arranged in approximately eight major sub- clusters. I then identified the sub cluster containing the target person. That cluster contained 33 individuals, five being well known to me as cousins whose MRCA’s are either my second great grandfather and grandmother or my third great grandparents on my second great grandmother’s side. Of the remainder, 11 had no tree, 4 had private trees, 5 had trees with no perceivable connection. These remain to be queried, but I suspect that they will mostly learn more about their ancestry from me than I will learn from them. Hopefully, we will be able to integrate them into the family tree.
One remaining cousin would probably have been revealed to me only through graphic analysis. In his tree is an ancestor who immigrated from Germany to Dayton five years prior to my second great grandfather. The spelling of his ancestor’s surname is a variant from mine, but I am looking forward to communicating with him to determine if he will have information that could break through my brickwall. It explains why my relative might have moved to Dayton Ohio after spending several months in Philadelphia. I have recently become aware of a Breidenbach in Philadelphia who immigrated in the same year as my second great grandfather, but apparently on a different ship. I am hoping that one of the other sub- clusters may lead me to cousins from that line.
Now, let me outline the steps I took to arrive where I am now. Starting with the identified sub cluster I went through each individual connected to my target cousin. I then copied their row from the vertices sheet onto a new standard Excel spreadsheet. I then copied the data from that spreadsheet and pasted it into a copy of my original Nodex spreadsheet on the vertices sheet. I then deleted subsequent rows in that sheet until the displayed graph contained few if any remaining vertices from other sub- clusters. This allowed me to visualize that subgroup more clearly. I recognize that all of that may not have been necessary, but it did give me a better understanding of what was in that cluster and how the graphic analysis works. I would appreciate any suggestions or criticisms before I proceed to further examine the other sub- clusters in the group.
Thank you again,
Bill Breidenbach
Hi Bill, Sorry for my slow reply! I don't always see replies on my older posts straight away. There are a few tricks in NodeXL that might help you. You can assign people to groups yourself if the grouping algorithms don't do quite what you think they should (I don't have it open right now - but look for the groups menu or right click often has options) and then on the groups worksheet you can turn individual groups on and off. No need to delete anything!
DeleteThat's a very exciting match to follow up on. It sounds very promising. I'm glad that the network graph approach has been useful for you! Best of luck with your research.